Foods That Trigger Irritable Bowel Disease (IBD)
Living with Irritable Bowel Disease (IBD), such as Crohn’s or colitis, can be a challenging journey. While medical advancements like Stelara offer relief, managing symptoms also involves paying attention to your diet. From heartburn relief to maintaining overall gut health, steering clear of certain trigger foods is crucial. Here’s a guide to five common culprits that may exacerbate IBD symptoms.
1. Greasy foods
Greasy and fried foods are often irresistible, but for those with IBD, they can spell trouble. High-fat content in these foods can lead to inflammation and irritation in the digestive tract, potentially triggering flare-ups. Swap out deep-fried favorites for grilled or baked alternatives to help minimize the impact on your gut.
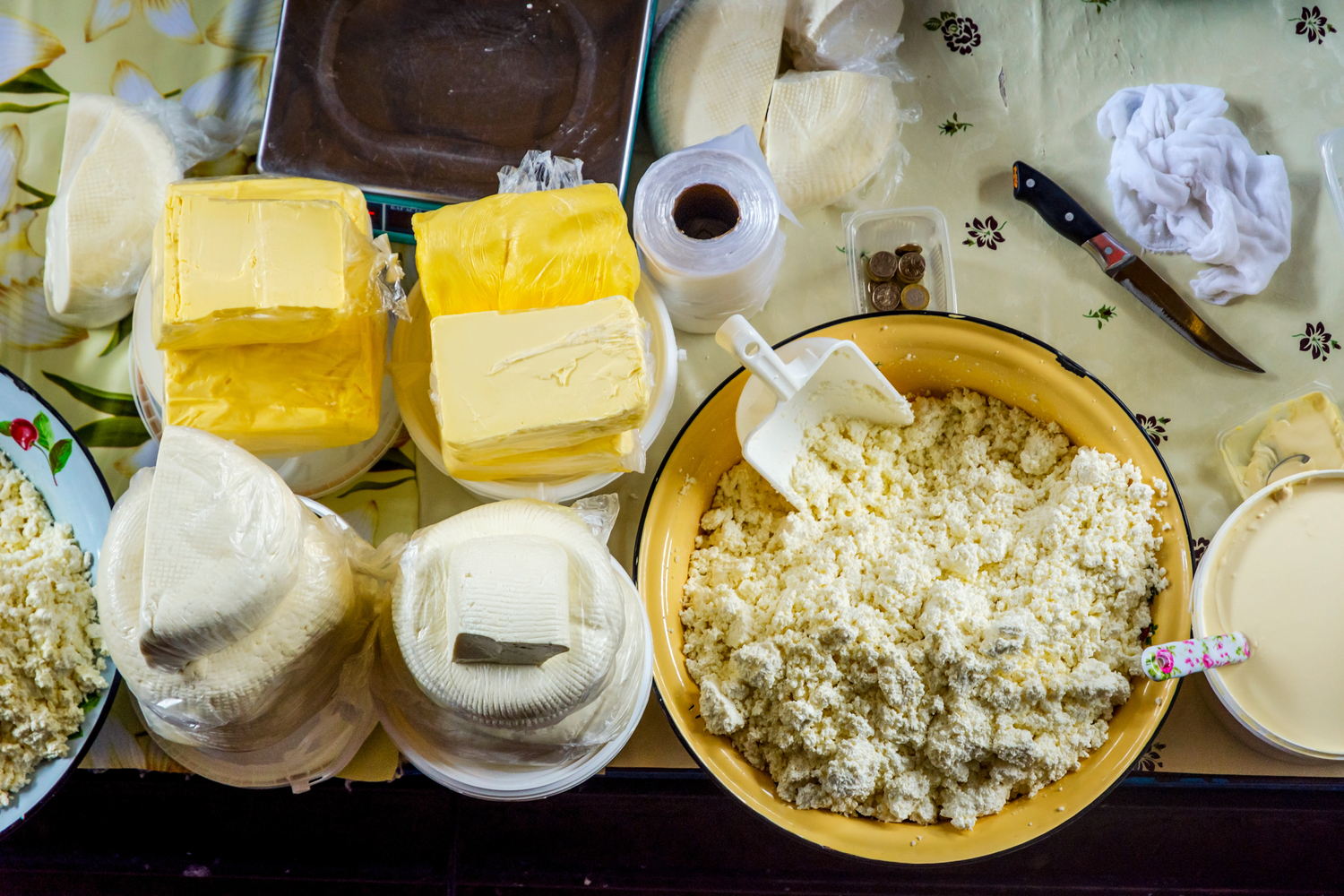
2. Dairy products
Dairy products can be a double-edged sword for individuals with IBD. While they are rich in calcium and other nutrients, they can also be difficult to digest, especially for those with lactose intolerance. Consider lactose-free or plant-based alternatives to ensure you get the nutritional benefits without the digestive distress. This simple switch may contribute to both heartburn relief and better overall gut comfort.
3. Wheat
Wheat and gluten-containing products are common staples in many diets, but for some with IBD, they can be triggers for discomfort. Research suggests that individuals with IBD may experience improved symptoms on a gluten-free diet. Explore gluten-free options like quinoa, rice, and gluten-free oats to maintain a diverse and satisfying diet without compromising gut health.
4. High-FODMAP vegetables
Certain vegetables are high in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs). For individuals with IBD, particularly those with sensitivity to FODMAPs, these vegetables can cause gas, bloating, and other digestive discomfort. Common high-FODMAP culprits include onions, garlic, and cruciferous vegetables. Opt for low-FODMAP alternatives like carrots, zucchini, and bell peppers to support a more gut-friendly diet.
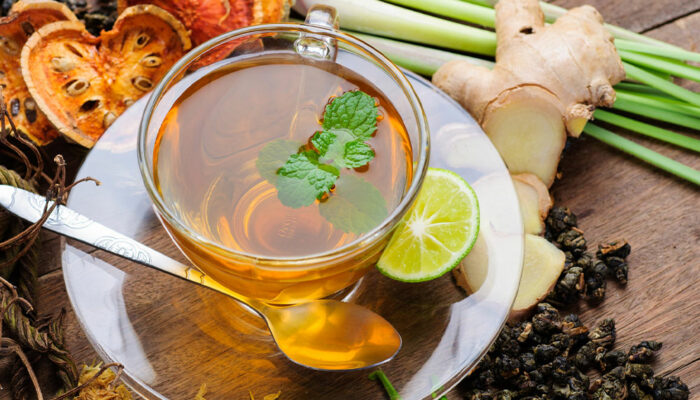
5. Caffeine
While a cup of coffee or tea can be a morning ritual for many, caffeine can be a potential trigger for IBD symptoms. It acts as a stimulant, potentially causing increased bowel movements and gastrointestinal irritation. Consider reducing your caffeine intake or opting for low-acid options like herbal teas to support better gut health.
Navigating life with IBD involves a multifaceted approach, and diet plays a crucial role in managing symptoms. Steering clear of trigger foods, such as greasy foods, dairy products, wheat, high-FODMAP vegetables, and excessive caffeine, can contribute to better gut health. While medications like Stelara offer relief at the medical level, making mindful dietary choices can enhance overall well-being. Keep in mind that individual responses to foods may vary, so it’s essential to work with healthcare professionals to tailor dietary recommendations to your specific needs. By incorporating these dietary adjustments, you can take positive steps toward achieving heartburn relief and fostering a healthier gut.