UTI – Warning Signs and Diagnosis Methods
Urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection that affects a person’s urinary tract organs, such as the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The disease is more common in women and can be painful. Thankfully, UTIs can be treated using simple antibiotics. In minor cases, the problem can also go away on its own without medication. This article discusses the different early warning signs of a UTI and the popular diagnosis methods.
Early warning signs
The following early warning signs can help identify UTIs:
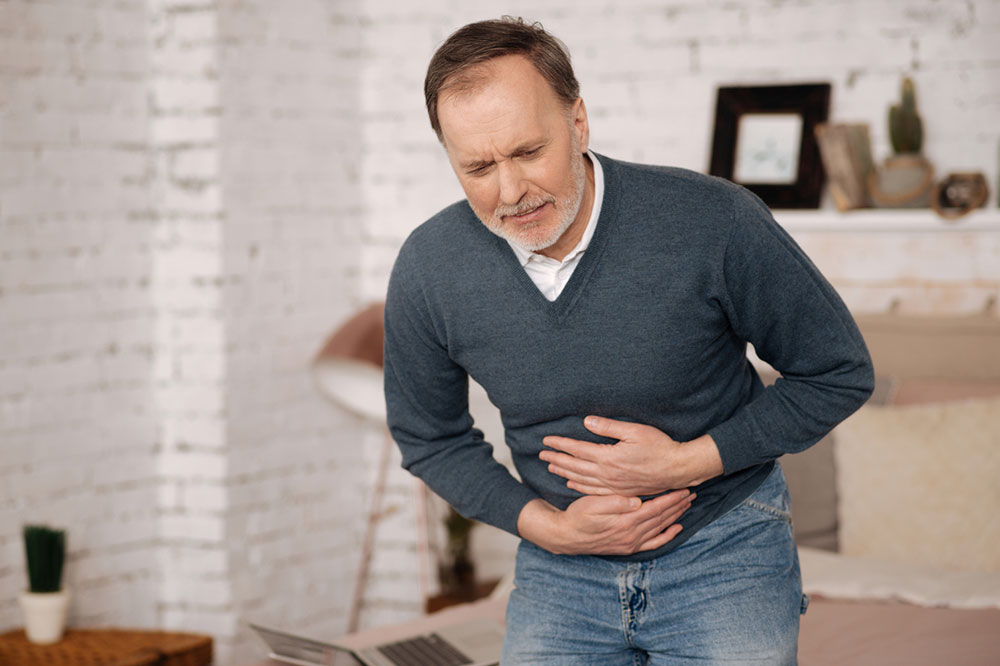
1. Pain or discomfort when urinating
This is the telltale sign of a UTI. The bacteria causing the infection irritates the lining of the urinary tract, resulting in inflammation. The inflammation, in turn, causes pain or discomfort when passing urine.
2. Change in color and smell of urine
The urine could become red, pink, or dark-colored due to the presence of blood. It might also become cloudy as the body tries to eliminate the excess white blood cells produced to fight the infection. In addition, the bacteria that cause the disease can give the urine a foul smell.
3. A strong and persistent urge to urinate
Due to the inflammation in the bladder and urethra, one might experience the continuous urge to urinate but still pass only a small amount of urine at a time. Elderly patients may have a lack of bladder control or urinary incontinence due to a UTI.
4. Fever and pain
As with all infections, fever, nausea, and vomiting are pretty common. Individuals with a UTI might also experience pain or pressure in the pelvis region similar to bloating. Groin, side, or upper back pain could also be reported.
Diagnosis
The following tests can be carried out to confirm the disease:
1. Analysis of urine sample
Here, a sample of the patient’s urine is analyzed in a lab to determine if it contains red blood cells, white blood cells, and bacteria. These are indicators of infections in the urinary tract.
2. Urine culture test
A urine culture test is usually carried out after a urine sample analysis to determine which bacteria is causing the infection and the medications that would be the most effective to combat it.
3. Imaging tests
If someone is frequently affected by UTIs, the doctor might recommend a CT scan, MRI, or ultrasound to check for abnormalities in the urinary tract. These scans are carried out using a contrast dye to ensure the organs and other details are visible.
4. Cystoscopy
For recurrent infections, medical practitioners might use a thin, long tube with a lens known as a cystoscope to examine the inside of the urethra and bladder.
One should be aware of and able to spot the warning signs of a UTI so that they can seek timely treatment. The condition can lead to severe complications if it progresses and spreads to the kidneys.